Japan is a country that is roughly the size of California and is stretched north to south. It is located in the Sea of Japan east of China and Korea and North of the Philippines. Because it is stretched north to south, it has 6 differing geographical zones. An example of its geographical differences can be seen in the difference between Okinawa, its western-most prefecture, a kind of tropic island, and Hokkaido, Japan's northern-most island which gets a good deal of snow in the winter. To display the difference in Japanese locations, we can examine the weather right now. Roughly noon at local time for each, Okinawa has 74°F with 54% humidity and windspeeds of 19 mph, Tokyo (roughly in the center of Japan on the main island of Honshu) has 65°F with 30% humidity and windspeeds of 4 mph, and Sapporo (located on the southern part of Hokkaido) has 57°F with 53% humidity and windspeeds of 4 mph. The landscape of Japan is one of the most beautiful in the world with its pine forests, good beaches, and mountains. The most famous of these mountains is Mount Fuji, recognizable by many across the world for its low slopes. Moreover, Japan tends to get a good amount of rain each year and gets big storms called "typhoons" in late summer to early fall. Japan also has many cherry blossom trees that blossom in the spring which many people go to see.
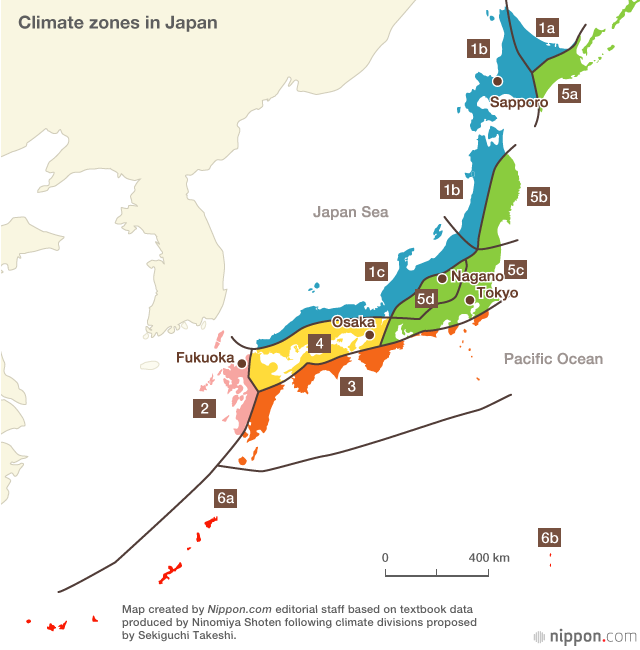
Image of Japanese climate zones. Okinawa is the red climate zone, Tokyo in the green, and Sapporo in the blue.
Image of Mount Fuji with its reflection in a lake.
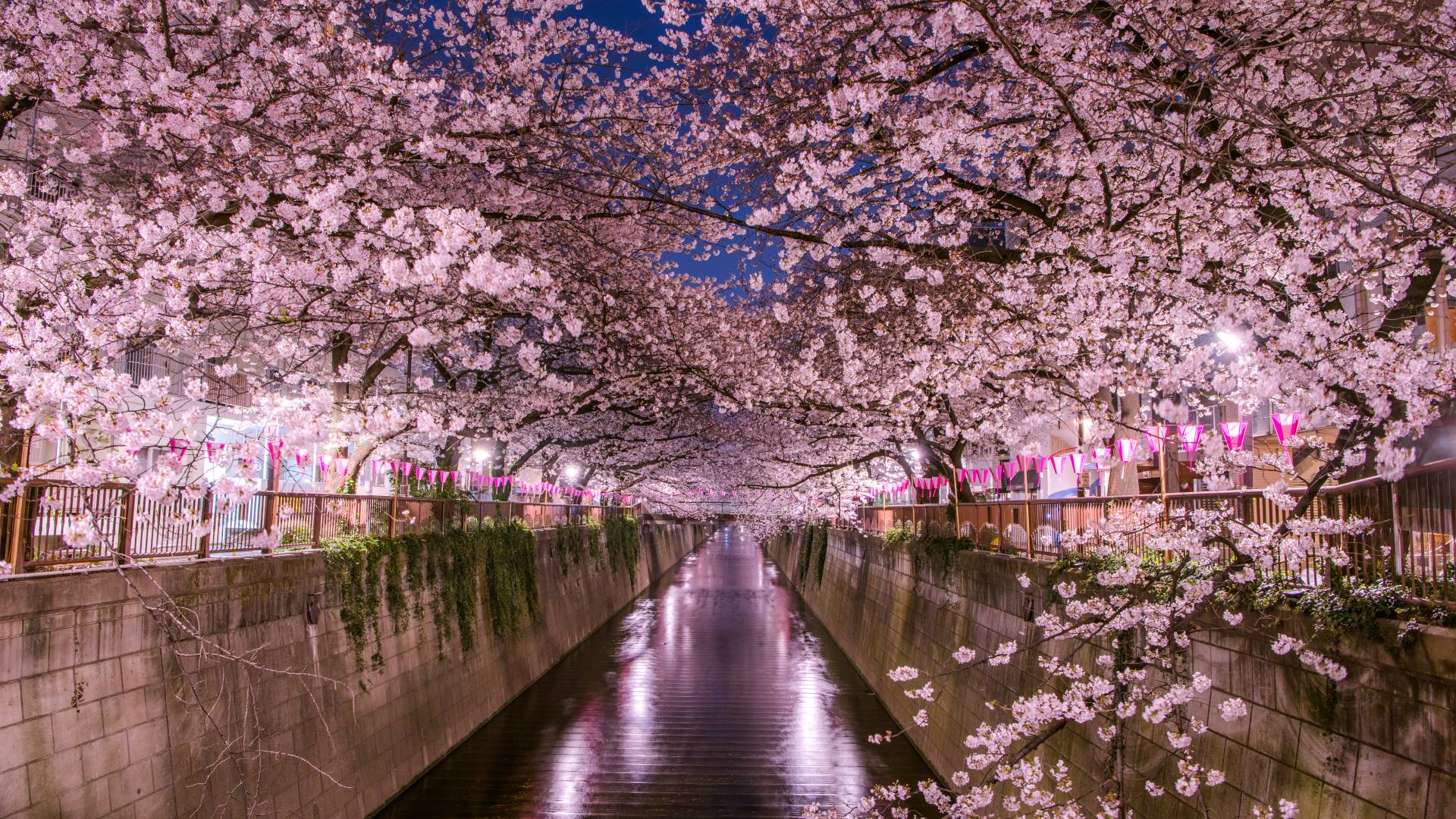
Cherry blossoms in Tokyo.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fuji-mountain-in-autumn-822273028-5a6a8a9c3418c600363958d3.jpg)

しゃしんはとてもきれいです!
ReplyDelete